The Evolution and Technology of Modern Displays
Content Index
Display screens have become an indispensable part of everyday modern life. But they have sometimes been sleeker and more high-tech looking.
Back in the day, bulky CRT monitors were the norm. Can you even imagine going back to those now? Screens have genuinely gone through a total transformation over the years.
Three main display innovations have pushed the boundaries of screen technology forward: LED, OLED, and UHD. Each one has revolutionized screens in their way.
For example, OLED smartphone screens give you those vibrant, eye-popping colors. UHD TVs deliver pictures with exact detail and an incredible range between the darkest and brightest areas. Plus, LED displays are generally more energy efficient compared to older alternatives.
In this post, we’ll dig deeper into understanding the science behind how these futuristic-sounding displays work their magic. We’ll geek out over their advantages and excellent capabilities. And we’ll discuss why they provide a mesmerizing viewing experience compared to old-school screens.
Whether you’re a tech-obsessed follower of the latest gadgets or just curious to learn what makes your screens so lovely to look at, this guide breaks down the need-to-know details about the leading display technologies of today—and probably tomorrow, too. Read on to enhance your appreciation for the screens lighting up our digital world!
-
1). The Genesis of Pixels: A Journey through Display Evolution
To understand modern display technologies like UHD, OLED, and LED, it’s essential to embark on a retrospective journey through the annals of display evolution.
This exploration is not merely about tracing the lineage of screens but about unraveling the fabric of innovation that has woven the very essence of how we visualize digital information today.
-
2). From Cathode Rays to Liquid Crystals: The Ancestral Lineage
The story starts in the late 1800s with the cathode ray tube (CRT), the most popular device for almost a hundred years. The way CRTs worked was by shooting electrons onto a glowing screen.
At the time, this innovative idea had several problems, including being too big, using too much electricity, and possibly harmful to health from radiation. To make panels that were less bulky, safer, and more energy efficient, liquid crystal display (LCD) technology was developed.
Linking liquid crystals that align to modulate light, LCDs marked a significant leap, offering lighter, more power-efficient devices capable of higher resolutions.
-
3). The Plasma Era: A Brief but Bright Interlude
In the late 20th century, plasma displays emerged as a contender, especially in large-screen televisions. Plasma screens, using small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases, offered superior brightness and better viewing angles than LCDs. However, their reign was short-lived due to high power consumption and susceptibility to screen burn-in.
-
4). The LED Revolution: A New Dawn
LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology emerged as the new millennium unfolded. LEDs used a backlighting technique for LCDs, replacing the traditional cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs).
Improvements in brightness and color reproduction, as well as energy efficiency, were brought about by this breakthrough. More colorful and interactive displays were possible because of LEDs, which ushered in a new age of display technology.
-
5). The Emergence of OLED: The Next Evolutionary Step
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes) technology, a more recent development, has taken the principles of LED and elevated them. By allowing individual pixels to emit light independently, OLEDs have eliminated the need for backlighting, resulting in screens that are thinner, more flexible, and capable of producing deeper blacks and more vibrant colors than ever before.
-
6). The UHD Leap: Beyond High Definition
Parallel to these technological advancements, Ultra High Definition (UHD) began redefining the standards of screen resolution. UHD, often synonymous with 4K, offered a resolution that was a quantum leap from the traditional 1080p Full HD, bringing unprecedented detail and realism to the screen.
-
7). The Convergence of Technologies: A Synergistic Future
We are now at a crossroads where these technologies meet. Present-day displays are built on top of the foundation that LED and OLED provide, while ultra-high definition (UHD) is pushing the limits of visual fidelity.
In addition to being an indicator of technological advancement, this convergence portends a future when the lines between the real and virtual worlds are less distinct.
-
1). Illuminating the World: The LED Display Revolution
In the vibrant tapestry of display technologies, LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays stand out as a pivotal innovation, transforming everything from television screens to giant billboards.
This section delves into the intricate world of LED displays, unraveling their workings, types, and profound impact on our visual experiences.
-
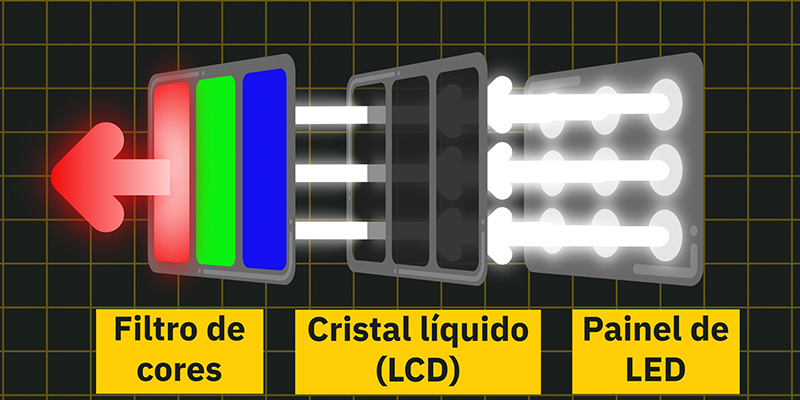
2). The Core of LED Technology: How It Lights Up Our Screens
At its heart, an LED is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. This simple yet effective mechanism radically departed from the bulky, energy-intensive CRT and plasma displays.
Millions of these tiny LEDs are used in LED displays to create images. The key lies in how these LEDs are controlled and manipulated to produce the vast spectrum of colors and brightness levels on our screens.
-
3). Types of LED Displays: From Mini to Micro
LED technology has evolved into various forms, each tailored for specific applications. The most common types include:
Traditional LED Displays: Used primarily for large outdoor screens with individual LEDs grouped to form pixels. Their robustness makes them ideal for digital billboards and signage.
Mini-LED Displays: As a refinement, Mini-LEDs are smaller than traditional LEDs and are used in backlighting LCD screens. This allows for finer control of local dimming zones, leading to better contrast and deeper blacks in LCD TVs and monitors.
Micro-LED Displays: Representing the cutting edge, Micro-LED technology uses microscopic LEDs to form individual pixels. This innovation promises higher brightness, exceptional color accuracy, and energy efficiency, potentially surpassing OLED in some respects.
-
4). Advantages of LED Displays: Why They Shine Brighter
LEDs have truly revolutionized everything when it comes to screens. Consider these fantastic advantages if you’re thinking about purchasing one.
First off, they use less energy than old-school displays. I’m talking like half or even less. Saving all that electricity goes hand in hand with saving some dollars on your utility bills.
And we can all appreciate the environmental perks of using less power. So, the energy efficiency factor alone makes LEDs super attractive.
LED displays are energy-smart, and they are also super durable. You won’t have to worry about frequently replacing them like other screens. These bad boys are made to stick around for the long run. They’ll work like champs for many years before needing a replacement.
Another major pro is that LED screens can get incredibly bright. We’re talking about easily visible under sunlight, bright. So, they work fabulously well for outdoor signs and billboards.
The colors also pop like crazy on them. Nowadays, you can find LED displays capable of producing colors even more accurately than old screens, which makes everything look more dynamic and vivid.
Overall, LED is the way to go when you want a long-lasting, energy-sipping display with excellent brightness and true-to-life color. Eco-friendly, wallet-friendly, and eye-friendly – LED checks all the boxes.
-
5). LED Displays in Action: From Living Rooms to Times Square
The applications of LED displays are diverse and widespread. In consumer electronics, they are the backbone of most modern TVs, computer monitors, and even some smartphone screens.
In the commercial realm, they light up advertising billboards and public information displays and are integral to event productions for their ability to deliver vibrant visuals in various lighting conditions.
-
1). The Art of Illumination: Unveiling the OLED Revolution
Regarding cutting-edge screen technology, OLED displays are stealing the show. You’ve probably heard the term OLED tossed around now and then when people talk about the latest TVs and smartphones.
But what makes OLED screens so epic? Simply put, they deliver mind-blowing colors, insane contrast, and more design flexibility than old-school displays.
These organic light-emitting diode displays are genuinely changing the whole game. The “OLED” name might sound weird and sci-fi. But don’t let that scare you off!
This post breaks down the need-to-know diets about this revolutionary tech in simple, everyday language. Consider this your beginner’s guide to understanding why OLEDs are wowing even the most tech-savvy among us.
We’ll learn how OLED screens work their vivid color magic versus traditional LCDs. We’ll spotlight all the best benefits that make even smartphone addicts and TV fanatics ooh and ahh over OLED. And we’ll peek at some of the wildly colorful, highly dynamic OLED innovations on the horizon.
-
2). The Essence of OLED: A Symphony of Light at the Pixel Level
OLED technology represents a significant leap from traditional display methods. Fundamentally, OLEDs consist of organic compounds that produce light in response to the application of electricity.
In contrast to LED/LCD screens, which necessitate a backlight, OLED displays possess self-illuminating pixels. This fundamental difference allows OLED displays to achieve unparalleled contrast and color depth.
-
3). The Color Spectrum Reimagined: How OLED Redefines Visuals
The self-emissive nature of OLED pixels means they can turn off completely to produce true blacks, a feat impossible for backlit displays. By increasing contrast and improving color reproduction, this capability not only enhances the vibrancy and lifelikeness of images but also improves their overall quality.
A color spectrum that erupts with unparalleled realism, the outcome is a visual encounter that is more in harmony with the inherent perception of the human eye.
-
4). Design Innovations: The Flexibility of OLED
OLED’s flexibility extends beyond its visual capabilities. The technology has enabled the development of thinner, lighter, and bendable displays.
This development has ushered in a novel era of design possibilities, wherein electronic devices are conceptualized and experienced in unprecedented ways (e.g., foldable smartphones and curved television displays).
-
5). The Challenges: Balancing Perfection with Practicality
Despite its advantages, OLED technology has its challenges. The organic materials used in OLEDs can degrade over time, potentially leading to issues like burn-in, where static images persist on the screen.
Additionally, the cost of producing OLED displays, particularly larger ones, remains higher than traditional LED/LCD screens, making them less accessible for specific market segments.
-
6). OLED in Action: A Spectrum of Applications
The utilization of OLED technology is present in an extensive array of devices. Precise for their design sophistication and superior image quality, OLED displays are a trademark of high-end smartphones and televisions in the consumer electronics industry.
Within the domain of professional displays, OLED monitors are favored by graphic designers, photographers, and video editors due to their exceptional color accuracy.
-
1). The Clarity beyond Compare: The UHD Experience
In display technology, Ultra High Definition (UHD) stands as a colossus, redefining the essence of image clarity and detail. This section delves into the world of UHD, unraveling its significance, the technological marvel behind it, and its profound impact on our viewing experience.
-
2). Defining UHD: A Resolution Revolution
So you’ve probably seen those TV ads going on and on about “4K” resolution. Well, let me decode what the heck they’re talking about! 4K is a nickname for what’s technically called UHD resolution.
These tech terms can get quite silly with all their labels. UHD packs four times as many pixels onto the screen as old-school HD screens. We’re talking over 8 million pixels filling up the display! My eyes hurt just thinking about it.
You might wonder why so many tiny pixels are jammed onto one screen. For starters, it makes every little detail in the picture startlingly clear and realistic. But it also fools your eyes in the best way possible.
You see when the pixels get so densely packed like that, your eyes can’t even tell them apart anymore at average TV-watching distances. So, instead of seeing a bunch of separate pixels, you see one ridiculously crisp, smooth, lifelike image that draws you right in.
So, in essence, UHD tech is so advanced now that it creates this crazy immersive viewing sensation that makes you feel like you’re looking through a window rather than watching a TV. Every scene, object, and texture looks almost accurate enough to reach out and touch!
-
3). The Journey from HD to UHD: A Visual Leap
Moving from plain old HD to the world of UHD isn’t just stepping up in technology – it’s entering a whole new dimension of quality.
Back in the day when HD was the hot new thing, its boosted detail blew people’s minds compared to the old blurry standard definition.
But UHD laughs in HD’s face when it comes to clarity. I’m talking textures so rich you feel like you can reach out and touch them. Colors so subtle and smooth it’s mesmerizing, and crystalline crispness down to the very last pixel.
Before UHD came along, you’d have to watch a mega-expensive cinema production to get that buttery smooth, ultra-refined picture.
Not anymore! Now, UHD brings a taste of that studio quality straight to your humble living room screen. We’re talking make-you-forget-you’re-watching-TV immersion.
Earnestly, gaze into the UHD promise land; it feels more like peeking through a window than staring at a screen. Scarily real-looking. Big, beautiful, and bursting with visual pop that goes above and beyond. That’s UHD in a nutshell.
-
4). The Impact of UHD: More than Just Resolution
UHD’s impact extends beyond mere pixel count. UHD has crushed it when setting new quality standards for important stuff like color accuracy, contrast, and overall visual wow factor.
A couple of slick technologies give it an edge over plain old HD.
For example, UHD displays can harness the power of HDR or High Dynamic Range.
This is a fancy term for making parts of the picture exponentially brighter or deeper and darker than old screens could. This translates to way more pop and dimension for images.
On top of that enhanced brightness range, UHD splashes screens with a crazy expansive spectrum of colors that HD could only dream of reproducing. We’re going from “nice rainbow” to “pot of gold” levels of vibrant, saturated, hyper-realistic colors shining off the display.
Between the boosted brightness capabilities and the massive color volume, UHD delivers images with such depth and dynamism that it’s nearly impossible to peel your eyes away. Every scene looks so lively and rich that you can reach in and touch the textures.
So whether it’s the amplified contrast, the cinematic colors, or the crystal apparent precision of over 8 million pixels – UHD is conquering visual entertainment across the board compared to outdated HD. The proof is in the stunning, drool-worthy picture.
-
5). UHD in Various Mediums: From TVs to Cinemas
The adoption of UHD has been widespread, spanning various mediums. UHD has become the standard for premium models in television, offering viewers an at-home cinematic experience.
UHD computer monitors are simply unmatched regarding detail for digital creators and artists. You could stare for hours and still spot spectacularly subtle color gradients, textures, and lighting effects in your designs that lower resolutions gloss over.
It’s visual candy for graphic designers, video editors, animators – any pro who thrives on high-definition greatness.
Even gamers are geeking over UHD’s ability to crank graphics to the next level. Who wouldn’t want to battle dragons or race supercars across stunningly realistic scenery? Talk about total immersion!
On the Hollywood side, moviemakers are also hopping on the UHD train. More and more blockbuster films are being shot natively in 4K and screened for audiences in top-tier UHD cinema halls.
And let me tell you, when done right, the big-screen UHD movie magic feels utterly captivating. Gorgeous cinematic worlds that feel as vibrant and lifelike as if you were on set as they yell “action!”
Indeed, UHD has spread its visual Midas touch far and wide. And with tech advancements charging forward every year, the ultrahigh definition still has so much more mind-blowing potential to unlock! Buckle up for the ongoing ride.
-
6). Challenges and Considerations in UHD Adoption
Despite its advantages, the adoption of UHD comes with considerations. The full benefits of UHD are best appreciated on larger screens and at closer viewing distances, which may only be feasible for some living spaces.
The availability of accurate 4K content is also still catching up, though it is rapidly growing with streaming services and UHD Blu-ray discs.
As we stand at the precipice of current technological advancements, the future of display technology beckons with promises of innovations that border on the realms of science fiction.
This section ventures into the emerging trends and potential breakthroughs poised to redefine our interaction with digital displays. Here’s a casual rewrite of the future display technology descriptions:
-
1). Dot Displays:
These new screens use tiny nano-crystals called quantum dots to take color quality to never-before-seen levels of vibrant, saturated goodness.
We’re talking about colors that are extremely rich and dynamic; HD colors seem washed out and boring in comparison! Quantum dots also amp up brightness big time. So expect quantum dot TVs and monitors to deliver exceptionally vivid, lifelike images that genuinely pop.
-
2). 8K Resolution:
Does UHD look wildly detailed? 8K kicks a considerable notch up by cramming in mind-melting 7680 x 4320 pixels! That’s four times the UHD pixel party. The content, specially shot in 8K, looks so real your brain can’t even process all the visual display information.
Down the road, prepare to get lost in surreal gaming worlds, experience intimate film shots that feel spookily present, and edit graphics with a level of zoom that reveals invisible details. The sheer pixel density will unlock new visual dimensions.
-
3). Holographic 3D Without Glasses:
No more wearing goofy 3D glasses to watch objects float off the screen! Future holographic displays will project startlingly realistic 3D images you can view from different angles, with no eyewear required.
Imagine flawlessly spinning 3D creations hovering in mid-air or full-motion holograms giving a lecture that looks beamed straight from the future. The applications for glasses-free 3D tech could revolutionize everything from medical imaging to product demonstrations.
-
4). E-Paper Video Displays:
E-paper and e-ink screens have mostly been static. But new advances are making them just as dynamic as traditional displays! Future e-papers could sport full-motion video, colorful images, and constant content refreshing with a paper-like reading experience that’s easy on the eyes. Think readable tablets that mimic print, low-energy billboards, and laptops that cause no eye strain.
-
5). Context-Aware Displays:
Can you imagine your screen adapting in real-time based on lighting conditions and whether anyone’s looking at it? Emerging context-aware displays will gauge what’s happening around them to automatically tune brightness, motion, colors, and more for the most comfortable viewing experience. Your displays could think for themselves to save power and enhance watchability.
-
6). AI-Integrated Displays:
With TVs and monitors becoming standard smart home hubs, soon, we’ll see them integrated with AI in incredible ways! AIs could personalize content for each viewer. Pull data from other connected devices.
Or even activate displays based on recognizing faces, motions, and frequently used apps. Imagine an AI that turns on your kitchen TV when it knows you’re cooking. That’s just a tiny peek at the convenience of AI-powered displays!
-
7). Sustainable Display Technology:
Finally, the display innovations of tomorrow won’t just be visually jaw-dropping – they’ll also be engineered from scratch for environmental friendliness.
Think components from recycled materials, manufacturing methods with lower carbon footprints, and panel designs requiring remarkably little energy to churn out brilliant visuals. The dream is fast, vibrant, cutting-edge displays that don’t cost the planet nearly as much. Here’s hoping display tech and ecology can coexist!
-
8). Predictions for the Next Decade:
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Integration:
The lines between physical and digital worlds will continue to blur, with AR and VR technologies becoming more integrated with traditional displays, leading to more immersive and interactive experiences.
-
9). Environmentally Sustainable Displays: With growing
Environmental concerns, the future will likely see a push towards more sustainable display technologies. This could include advances in manufacturing processes, more eco-friendly materials, and technologies that consume less energy.
Personalized Display Experiences: Future displays might adapt to our physiological and psychological preferences, offering personalized viewing experiences optimized for visual comfort and content relevance.
-
1). Navigating the Maze of Modern Display Technology
Selecting the appropriate display can be likened to navigating a labyrinth in the current technological landscape, where the market is inundated with countless alternatives.
To assist you in choosing a display that not only fulfills your requirements but also elevates your viewing experience, this section endeavors to clarify the procedure by providing guidance and insights.
-
2). Understanding Your Needs: The First Step in Selection
The journey to selecting the perfect display begins with clearly understanding your needs. Are you a gamer seeking a display with lightning-fast response times?
A professional graphic designer in need of impeccable color accuracy? Or a casual viewer looking for an all-around performer? Identifying your primary use case is crucial in narrowing down your options.
-
3). Size and Resolution: The Cornerstones of Display Quality
Size Matters: The size of the display is a critical factor. Larger screens offer more immersive experiences, particularly for gaming and cinematic viewing. However, the size should harmonize with your viewing distance and space constraints.
Resolution Revolution: Higher resolution means more pixels, translating to sharper and more detailed images. While 4K or UHD is becoming the norm, especially for screens above 27 inches, Full HD (1080p) may suffice for smaller screens or if budget constraints are a consideration.
-
4). Panel Types: Decoding the DNA of Displays
Displays come in various panel types, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
• IPS (In-Plane Switching): Known for excellent color accuracy and wide viewing angles, IPS panels are ideal for tasks that demand color precision, such as photo editing and graphic design.
• TN (Twisted Nematic): These panels offer the fastest response times and high refresh rates, making them a favorite among gamers, albeit at the cost of color accuracy and viewing angles.
• VA (Vertical Alignment): VA panels strike a balance with better contrast ratios and color depth than TN panels, though they lag slightly in response time.
-
5). Technology Type: LED, OLED, or QLED?
LED/LCD: The most common and budget-friendly option, offering good picture quality and energy efficiency. Ideal for general use and office work.
OLED: Offers superior contrast ratios and true blacks, making them perfect for high-end TVs and premium monitors. However, they come with a higher price tag.
QLED (Quantum Dot LED): A variant of LED displays enhanced with quantum dot technology, providing brighter and more vibrant colors. An excellent choice for both general use and entertainment.
-
6). Additional Features to Consider
Refresh Rate: Important for gaming and high-speed content, with higher rates offering smoother motion.
Connectivity: Ensure the display has the correct ports (HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-C) for your needs.
Ergonomics: Adjustable stands, eye comfort features, and screen curvature can enhance viewing comfort.
Intelligent Features: Smart capabilities like built-in streaming and voice control might be desirable for TVs.
In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, the impact of display technology on our planet is a topic of increasing significance.
This section delves into the ecological footprint of display manufacturing, the sustainability efforts within the industry, and the future of eco-friendly display technologies.
-
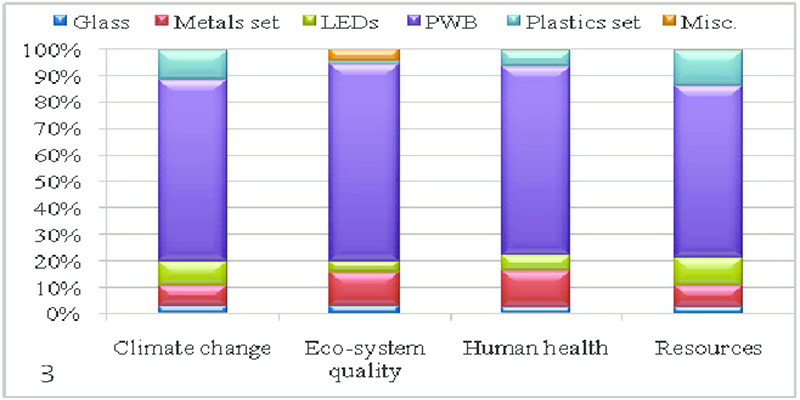
1). Resource Extraction and Consumption
• Rare Earth Elements: Displays, especially those with advanced technologies like OLED and quantum dots, often require rare earth elements. Mining these elements can lead to substantial environmental degradation, including soil and water pollution.
• Metals and Plastics: Metals like aluminum, copper, and various plastics are prevalent in display manufacturing. The extraction and processing of these materials contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental pollutants.
-
2). Energy Intensive Production Processes
• Manufacturing Energy Use: The production of displays, particularly those with high-resolution and large sizes, is energy intensive. This energy consumption contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the devices.
• Supply Chain Emissions: The global supply chain producing displays, from raw material extraction to assembly and shipping, adds significant greenhouse gas emissions.
-
3). Chemical Usage and Pollution:
• Hazardous Chemicals: Several chemicals utilized in displaying displays are hazardous to human health and the environment. Irrespective management and disposal of these substances may result in ecological degradation and contamination.
• Water Pollution: Wastewater generated during the manufacturing process frequently comprises metals, solvents, and additional contaminants that, if not appropriately treated, can contaminate water sources.
-
4). E-Waste and Challenges in Disposal:
• Short Product Lifecycles: With rapid technological advancements, displays often become obsolete quickly, leading to increased e-waste as consumers upgrade to newer models.
• Recycling Challenges: Displays are composed of a complex mix of materials, making them difficult to recycle. This complexity often leads to inadequate recycling and dumping of old displays in landfills, where they can leach toxic substances.
-
5). Packaging and Transportation:
• Packaging Materials: The packaging of displays, often involving plastics and other non-biodegradable materials, contributes to waste and environmental impact.
• Carbon Footprint of Transportation: The global distribution of displays adds to the carbon footprint, with emissions from transportation contributing to climate change.
-
6). Energy Consumption in Use:
• Power Usage of Displays: The energy consumption of displays while in use, especially for more extensive and brighter screens, is a significant factor in their overall environmental impact.
• Standby Power Consumption: Many displays continue to consume power even in standby mode, contributing to unnecessary energy use.
Energy-Efficient Technologies: The industry is shifting towards more energy-efficient technologies like LED and OLED, which consume less power than older CRT and plasma screens. Features like automatic brightness adjustment and energy-saving modes are becoming standard.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Efforts are underway to use more sustainable materials in display production. This includes reducing the use of hazardous substances and researching biodegradable or recyclable components.
Extended Lifespan and Repairability: Manufacturers focus on extending displays’ lifespan and making them easier to repair. This approach reduces waste and decreases the environmental impact over the product’s life cycle.
Solar-Powered and Self-Sustaining Screens: Research is being conducted into displays that can generate their power, potentially through integrated solar cells. This innovation could significantly reduce the energy consumption of electronic devices.
Organic and Biodegradable Displays: There is ongoing research into organic display materials that are less harmful to the environment. The goal is to develop screens that can be safely decomposed or recycled at the end of their lifespan.
Innovations in Recycling: Advances in recycling technologies are crucial for reducing the environmental impact of displays. This includes more efficient methods of separating and reclaiming materials and designing displays with recycling in mind.
Regulatory and Industry Standards: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly setting energy efficiency and environmental safety standards in display manufacturing. Compliance with these standards is becoming a critical factor in the industry.
In summary, the future of display technology is embraced. It is evident that we are concluding an extraordinary epoch in the development of visual media as we examine LED, OLED, and UHD display technologies.
Digital displays are characterized by diversity and dynamism, as each technology brings advantages and innovations.
LED displays have established themselves as a dependable and adaptable foundation within display technology. On a broad spectrum of applications—from large-scale digital signage to commonplace consumer electronics—they are a practicable option due to their energy efficiency and longevity.
OLED Displays, with their unparalleled ability to produce true blacks and vibrant colors, have redefined what we expect from high-end screens.
The flexibility and thinness of OLED technology continue to push the boundaries of design and functionality, leading us into a future where displays are not just seen but also felt and interacted with in novel ways.
UHD Technology has elevated the standard for visual clarity and detail. It has transformed our viewing experience, bringing cinematic quality into our homes and making ultra-high definition the new benchmark for content creators and consumers.
As we look to the future, the convergence of these technologies and emerging trends like flexible and transparent displays, AI integration, and sustainable manufacturing promises an even more immersive and interactive visual landscape.
The challenge and opportunity lie in responsibly harnessing these advancements, ensuring that as we pursue higher resolution and more vivid displays, we also remain mindful of our environmental impact.
In simple terms, the exploration of UHD, OLED, and LED displays encompasses more than mere technological progress; it unveils novel opportunities that revolutionize narrative construction, interpersonal interaction, and artistic manifestation.
By adopting these technologies, we enter a forthcoming era in which the displays in our vicinity serve as entrances to experiences that are more immersive, personal, and relevant to our daily lives rather than simple windows to digital content.
Rental RS Series
Brand New Design, Better Stability
P1.95mm to P4.81mm – Indoor & Outdoor LED Display for Rent