DisplayPort vs HDMI: Which is Better for LED Display?
DisplayPort and HDMI are two common and easily confused types of data transmission interfaces. This article will compare them from multiple perspectives to help you make a confident choice when selecting device interfaces.
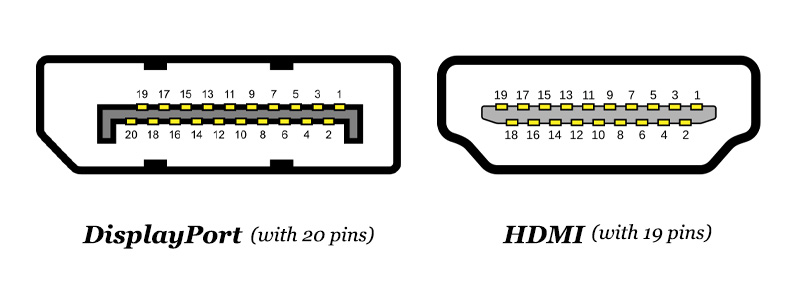
- DisplayPort: DisplayPort is a digital video interface standard designed to replace VGA, DVI, and FPD-Link (LVDS). It transmits audio, video, or USB data from a computer host to a display device through 20 signal pins.
- HDMI: HDMI is a fully digital audio and video transmission interface that can send uncompressed audio and video signals through 19 signal pins.
- DisplayPort interface standard was introduced in 2006 by VESA, the alliance of PC and chip manufacturers. It requires no certification and no royalties. Hardware manufacturers such as AMD, Apple, Dell, Intel, Lenovo, and HP support DisplayPort.
- HDMI standard debuted in 2002 and was led by TV manufacturers like Hitachi, Matsushita (Panasonic), Quasar, Philips, Sony, and Toshiba. Adopters of HDMI are required to pay a $10,000 annual patent fee.
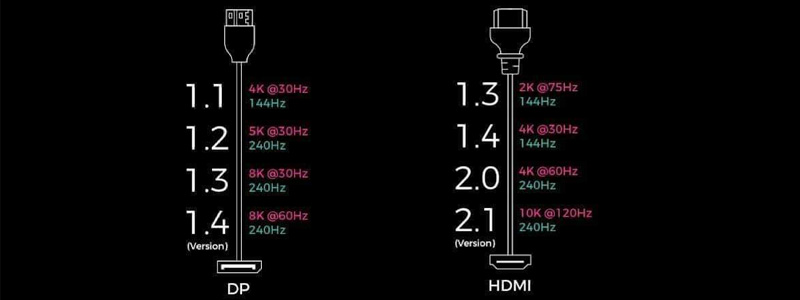
| DisplayPort
Version |
Release Date | Bandwidth | Maximum Transfer Rate | Maximum Resolution/Refresh Rate | Maximum Transmission Distance | Features |
| DisplayPort 1.0-1.1a | 2006/2008 | 10.8 Gbps | 8.64 Gbps |
|
2m |
|
| DisplayPort 1.2-1.2a | 2010/2012 | 21.6 Gbps | 17.28Gbps |
|
15m |
|
| DisplayPort 1.3 | 2014 | 32.4 Gbps | 25.92 Gbps |
|
Supports 4.5 meters of optical fiber cable. |
|
| DisplayPort 1.4-1.4a | 2016/2018 | 32.4 Gbps | 25.92 Gbps |
|
Supports 4.5 meters of optical fiber cable. |
|
| DisplayPort 2.0-2.1 | 2019/2022 | 80 Gbps | 77.37 Gbps |
|
|
|
| DisplayPort 2.1a | January 2024 | 80 Gbps | 77.37 Gbps |
|
Supports 2-meter passive cable. |
|
| HDMI/Version | Release Date | Bandwidth | Maximum Transfer Rate | Maximum Resolution/Refresh Rate | Features |
| HDMI 1.0-1.1 | 2002/2024 | 4.95 Gbps | 3.96 Gbps |
|
|
| HDMI 1.2-1.2a | 2005 | 4.95 Gbps | 3.96 Gbps |
|
|
| HDMI 1.3-1.3a | 2006 | 10.2 Gbps | 8.16 Gbps |
|
|
| HDMI 1.4-1.4a-1.4b | 2009/2010/2011 | 10.2 Gbps | 8.16 Gbps |
|
|
| HDMI 2.0-2.0a-2.0b | 2013/2015/2016 | 18 Gbps | 14.4 Gbps |
|
|
| HDMI 2.1-2.1a-2.1b | 2017/2022/2023 | 48 Gbps | 42.6 Gbps |
|
|
4.1 DisplayPort includes 4 forms:
- Standard DisplayPort;
- Mini DisplayPort (MiniDP) (introduced by Apple Inc. in 2008);
- USB Type-C (popular since 2015);
- Thunderbolt: Initially developed by Intel and Apple, but the latest version Thunderbolt 3 is solely by Intel.
4.2 HDMI includes 5 forms:
- Type A: 19 pins, 4.45 mm × 13.9 mm, widely used in daily applications.
- Type B: 29 pins, 4.45 mm × 21.2 mm;
- Type C (Mini HDMI): 19 pins, 2.42 mm × 10.42 mm, mainly used in digital cameras;
- Type D (Micro HDMI): 19 pins, 2.8 mm × 6.4 mm;
- Type E: 19 pins, 4.45 mm × 13.9 mm, used in automotive video systems.
- HDMI supports nearly all high-fidelity lossless audio formats: PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), Dolby Digital (AC-3), Dolby Digital Plus (E-AC-3), Dolby TrueHD, DTS (Digital Theater Systems), DTS-HD Master Audio, AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), and L-PCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulation).
- DisplayPort supports audio formats including PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), Dolby Digital (AC-3), DTS (Digital Theater Systems), and L-PCM (Linear Pulse Code Modulation).
- DisplayPort is suitable for professional audio setups requiring many speakers due to its support for more audio channels (DisplayPort 1.4 can handle up to 128 audio channels).
- DisplayPort cables have the same basic layout and wiring, supporting similar functionalities: audio, daisy chaining, G-Sync / FreeSync, HDR, and DSC.
- DisplayPort cables operate in seven transmission modes (RBR, HBR, HBR2, HBR3, UHBR10, UHBR13.5, and UHBR20).
- DisplayPort cables are certified by VESA and come in various categories: Standard, DP8K, DP40, DP54, and DP80.
- HDMI offers standard HDMI cables (19 pins), as well as fiber optic HDMI cables or wireless HDMI cables (using transmitter and receiver connectors).
- 7.1 DisplayPort is widely used in fields requiring high resolutions and refresh rates, such as high-speed gaming consoles, professional graphic design monitors, high-performance graphic and video editing (virtual reality and augmented reality devices), as well as broadcasting, monitors, medical, precision instruments, and military equipment.
- 7.2 HDMI dominates in consumer electronics and entertainment systems, extensively used in set-top boxes, TV boxes, DVD players, personal computers, cameras, video processors, projectors, digital audio systems, and home theater systems. With the popularity of 8K TVs, HDMI 2.1 is set to become the most universal multimedia interface.
LED displays require data and information to be processed and optimized by a video processor, then converted and distributed in the appropriate format. Various video sources can feed into the video processor, such as computer monitors, video recorders, game consoles, video conferencing equipment, and surveillance cameras.
Therefore, for ultra-high resolution led displays; for example, a video wall in a conference room measuring 7.2*4.05 meters uses our Indoor Display XA600-Series with P0.93 led panels stacked together, this setup achieves a total pixel count of 7680*4320 pixels; the video processor’s input interfaces must support DisplayPort and HDMI (like Novastar’s VX series) to perfectly accommodate different connections.
For led displays with resolutions lower than 1920*1080 (4K), for instance, an outdoor advertising screen measuring 7.68*4.8 meters uses our FV960-Series Outdoor Display with P5.7 panels. The total pixel count is 1344*840 pixels; usually only an HDMI input (like Novastar’s TB series) is required.
Indoor Display XA600-Series
![]() Front-end Convenient Maintenance
Front-end Convenient Maintenance
![]() Cabinet Size: 600*337.5mm/16:9 Ratio
Cabinet Size: 600*337.5mm/16:9 Ratio
![]() Compatible with 300*168.75mm Module
Compatible with 300*168.75mm Module
![]() With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
FV960-Series Outdoor Display
![]() Front-end Convenient Maintenance
Front-end Convenient Maintenance
![]() Cabinet Size: 960*960mm
Cabinet Size: 960*960mm
![]() Compatible with 480*320mm Module
Compatible with 480*320mm Module
![]() With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
With 3 Years Warranty and 5% Spare Parts
9. In conclusion
DisplayPort is commonly used in high-performance computers and professional display devices because it supports multi-stream transmission. HDMI is more focused on consumer electronics and home entertainment systems. Consider compatibility and usage scenarios carefully when choosing the appropriate interface for your device.
Contact
 Building D, Hongfa Science Park,
Building D, Hongfa Science Park,
2035 Songbai Road, Shiyan, Bao’an District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.