Learning is a joy, let’s dive into led display technology together!
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy as photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photon) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the semiconductor’s band gap.
The first practical LEDs were developed in 1962, emitting low-intensity infrared light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote control circuits for various consumer electronics. Modern LEDs cover visible, ultraviolet, and infrared wavelengths with high light output.
Compared to incandescent light sources, LEDs have many advantages, including lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, greater physical robustness, smaller size, and faster switching. LED applications are vast, including aviation lighting, automotive headlights, advertising, general lighting, traffic signals, camera flashes, lighted wallpaper, plant grow lights, and medical devices.
What is an LED Display?
LED displays are versatile screens that use Light Emitting Diodes to produce vibrant and high-resolution visuals. They are widely used for advertising, events, and informational displays due to their bright, clear images and energy efficiency.
LED displays come in various sizes and configurations, suitable for both indoor and outdoor environments, making them ideal for concerts, trade shows, sports arenas, and public information boards. Their durability and long lifespan ensure reliable performance even in demanding conditions.
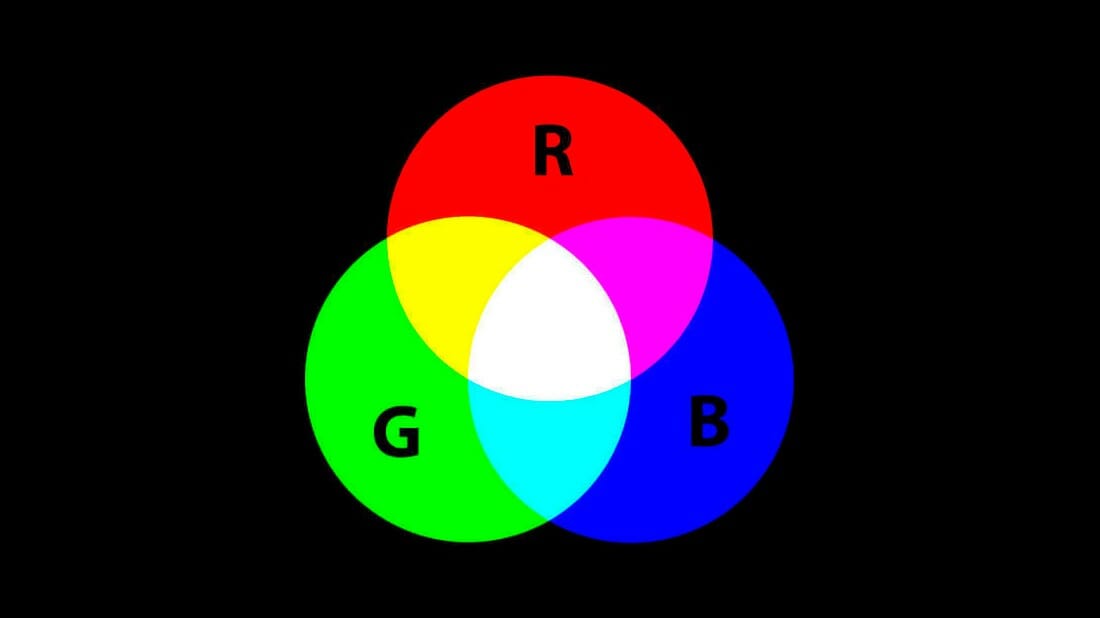
What is RGB?
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, the primary colors of light used in electronic displays and imaging. By combining different intensities of these three colors, a wide spectrum of colors can be created.
RGB is the foundation for digital screens, cameras, and lighting systems, enabling the accurate and vibrant display of images and videos. This color model is essential for various applications, from television screens and computer monitors to led displays and color printing.
How do LED Display Work?
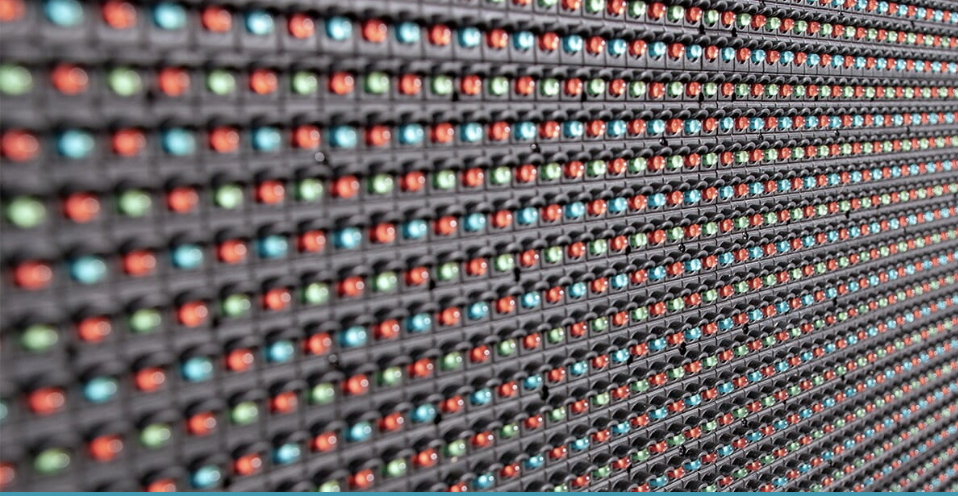
LED displays are made up of many tightly packed LEDs. By adjusting the brightness of each LED, the diodes together create an image on the screen.
To produce bright, colorful images, LED displays use the principle of additive color mixing, where new colors are created by mixing different colors of light. The screens consist of red, green, and blue LEDs arranged in a fixed pattern. These three colors together form a single pixel. By adjusting the intensity of each diode, billions of colors can be produced. When viewed from a distance, the many colored pixels merge to form an image.
What is Pixel Pitch and Screen Solution?
![]()
The distance between the LED screen diodes determines the resolution of the screen. From the center of each set of red, green, and blue diodes, the distance to the center of the adjacent group is measured. This distance is called the pixel pitch. Each set of diodes together form a pixel – or pixel
If the LED screen has a pixel pitch of 1 cm, each pixel can have 100 x 100 pixels. Square screen. The resolution on the screen is set to the number of pixels in height and width. If your screen is 6 x 8 meters and the pixel spacing is 1 cm, the resolution is 600 x 800 pixels.
Image Resolution
Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail.
Resolution refers to the number of pixels in an image. Resolution is sometimes identified by the width and height of the image as well as the total number of pixels in the image. For example, an image that is 2048 pixels wide and 1536 pixels high (2048 x 1536) contains (multiply) 3,145,728 pixels (or 3.1 Megapixels).
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly resolved. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes , to the overall size of a picture, or to angular subtense.
The measure of how closely lines can be resolved in an image is called spatial resolution, and it depends on properties of the system creating the image, not just the pixel resolution in pixels per inch (ppi). In effect, spatial resolution refers to the number of independent pixel values per unit length.
![]()
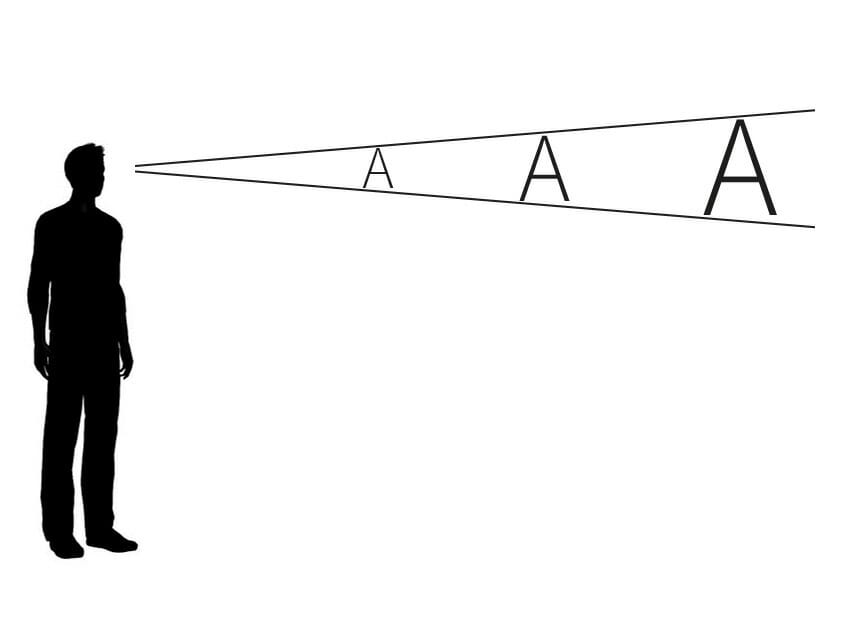
Viewing Distance
According to the working environment, led displays can be divided into indoor led screens, outdoor led screens and semi-outdoor led screens. There are some data in theory which can reflect the relationship between the pixel pitch and the best viewing distance.
In the actual application, because of the limitation of led display installation environment and identify ability, led display’s smallest viewing distance is mean the shortest distance that can identify the text and picture showing.
Which Solution Should I Choose?
The resolution required on the led screen depends on the viewing distance. From what distance does your viewer watch the screen? If you are close to a low resolution led display (the distance between the diodes is large), it is difficult to decode the screen content.
Usually, there is a connection between screen resolution and price. The higher the resolution, the more .m2 per diode – hence the higher square price.
If you install a digital signage on a main road or building facade, you can see it from a distance. Here, there is no need for a screen with high resolution – and it is unnecessarily expensive. If it is the floor height screen in the middle of the department store, the audience will get closer and closer. Here, the high resolution screen works best.
A rule of thumb for led screens is to observe a distance of 1 mm per meter.
Energy Efficient Technology
LED is a highly energy-efficient technology, which is why LED bulbs are so common today. The power consumption of the diodes in an led display depends on the type of screen, brightness, and usage.
There are many types of LEDs and screens. For example, indoor displays and outdoor digital signs visible in direct sunlight have different power consumption. Screen brightness also has a significant impact. The image needs to be clear, but the screen should not be glaring. Outdoor led displays are much brighter during the day than after sunset.
Where is the LED Screen Kept?
Since many factors work, it is difficult to generalize the life of the LED screen. But maintaining the screen properly can easily last for more than a decade. As with all forms of electronics, life expectancy is also affected by everyday use and the environment around the screen. Brighter images and high brightness levels wear more on the screen than darker images and lower light levels. In addition, factors such as humidity and salt content in the air can play a role.
During the lifetime of the LED screen, the light output of the diode will decrease. How much depends on the type and generation of the diode. Many LED screens never use full light intensity, so the reduction is rarely a problem.
What is IP Rating for LED Display?
The IP Code, or International Protection Marking, IEC standard 60529, sometimes interpreted as Ingress Protection Marking, classifies and rates the degree of protection provided by mechanical and electrical enclosures against intrusion, dust, accidental contact, and water. It is published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
This standard provides more detailed information than vague marketing terms like “waterproof.” For example, an IP68-rated phone is “dust-tight” and can be “immersed in 1.5 meters of freshwater for up to 30 minutes.”
● First Digit: Solid Particle Protection
The first digit indicates the level of protection the enclosure provides against access to hazardous parts (e.g., electrical conductors, moving parts) and the ingress of solid foreign objects.
● Second Digit: Liquid Ingress Protection
The second digit indicates the level of protection against harmful water ingress. Waterproof ratings above IPX6 are not cumulative. A device that meets IPX7 (immersion in water) does not need to meet IPX5 or IPX6 (water spray exposure). Devices that meet both tests will list them separated by a slash, such as IPX5/IPX7.






 Mob/Whatsapp:
Mob/Whatsapp:  Building D, Hongfa Science Park,
Building D, Hongfa Science Park,