Do LED Lights Get Hot?
Don’t you find it fascinating when someone shows you how many LED bulbs they have in their house? LED lights are always a better choice over incandescent or fluorescent bulbs. You will commonly find them in appliances like computers, cars, and televisions. But are they just great because of their appealing colors? Nope, they are also good because they save a lot of energy. You can pretty much expect these lights to last for a very long time.
But do you wonder if LED lights overheat? This question looks simple but can surprisingly have a detailed answer. To understand the science behind these lights, let’s compare them to other types of lighting to understand how their temperature affects their performance and safety.
1. Understanding How LED Lights Function
You first need to understand how these lights work to see if they get hot. The word ‘LED’ generally stands for Light Emitting Diode. Traditional incandescent bulbs create light by heating a filament, but LED lights do not involve heat. They make light by using a process called electroluminescence. This process involves passing an electrical current through a semiconductor material, which then gives out light.
Because LEDs do not rely on heat to produce light, they are much more efficient when it comes to converting energy into light. Incandescent bulbs waste quite a lot of energy as heat. But LEDs use most of the energy to produce light. This is a good reason why LEDs are much cooler to the touch than traditional light bulbs you come across.
LED lights work like this: when you turn the switch on, electricity travels through the wires to the LED bulb, which then lights up. That is what makes the bulb produce light. But when you turn the switch off, the energy stops flowing freely to your LED light. This makes the entire process stop as well.
Do LED Lights Get Hot?
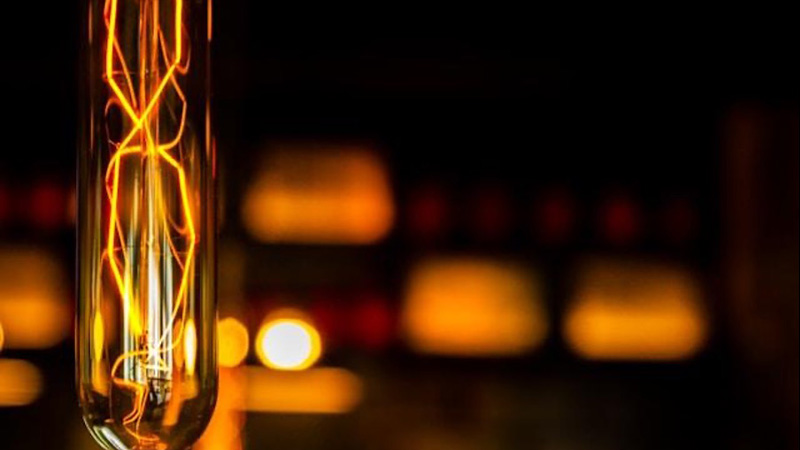
The short answer is yes, LED lights do get hot. But not in the same way as incandescent or halogen bulbs. The heat created by an LED light is less intense and is mainly concentrated at the base of the bulb. This is where the electronics and heat sink are located, rather than on the bulb’s surface.
The LED beam itself does not generate heat. So, these lights stay cooler in comparison to incandescent or halogen bulbs. While incandescent bulbs get as hot as 200-250°C (392-482°F), LED bulbs usually stay much cooler and operate at around 30-60°C (86-140°F). Because LEDs run at a lower temperature, they are less likely to cause any burns or start a fire. This is why they are a safer choice for many uses.
Why Do LED Lights Get Hot?
Even though LEDs are more efficient, they are not 100% efficient. Some of the energy used by the LED is still converted into heat, but you will notice it to be much less as compared to other bulbs. The heat produced by an LED light mainly comes from the energy lost in the semiconductor material and the electronic components that power the LED.
Most of this heat is generated at the junction where the light is formed, known as the p-n junction. However, if this heat is not properly managed, it can reduce the light output and shorten the overall lifespan of the LED.
2. How is Heat Managed in LED Lights?
Manufacturers build LED lights with cooling systems so that they last longer. One of the best ways to manage heat is by using a heat sink. These heat sinks are made from aluminum. They pull heat away from the LED chip and spread it out into the air. This keeps the LED chip cool and prevents it from overheating.
Some LED bulbs also use cooling fans or other cooling technologies to dissipate heat in other different ways. Such systems allow LED lights to function at higher brightness levels without compromising their lifespan or safety.
3. Comparing LED Lights to Other Types of Lighting
Let’s check how the heat generation of LED lights differs from other types of lighting:
Incandescent Bulbs:
As we mentioned earlier, incandescent bulbs build a significant amount of heat. This heat comes from the filament inside the bulb getting so hot that it glows and emits light. But because they lose so much energy as heat, they are much less efficient than LEDs.
Halogen Bulbs:
Halogen bulbs fall under the category of incandescent light bulbs. These bulbs get hotter than normal incandescent bulbs because they run at higher temperatures which makes them dissipate a lot of heat. You should use these bulbs in areas where bright light is needed. But keep in mind that they become dangerously hot!
Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs):
It is safe to assume that CFLs are better than incandescent bulbs because they emit less heat. But they still produce more heat than LEDs. Keep in mind that the mercury in CFLs can be harmful if the bulb breaks.
LED Bulbs:
LEDs are the best bulbs you may find. They need less energy because they produce very little heat. You also don’t have to worry too much when you are using them in other applications.
![]() Energy Saving Display 30% Design
Energy Saving Display 30% Design
![]() Standard Modules Front/Rear Service
Standard Modules Front/Rear Service
![]() Standard Size: 500×250/1000*1000mm
Standard Size: 500×250/1000*1000mm
![]() Display Can Operate at -20°C to 60°C
Display Can Operate at -20°C to 60°C
4. Why Does the Temperature of LED Lights Matter?
The temperature of an LED light also affects other important factors. It greatly influences the color, brightness, and lifespan of the light.
Color Temperature:
The color temperature of an LED light is measured in Kelvin (K). You will find warmer colors to have a lower Kelvin rating (around 2700K). But colors that are cooler will have a higher Kelvin rating (around 5000K).
Brightness:
The brightness of LEDs is measured in lumens. It starts to decrease if the LED gets too hot. Heat will shorten the lifespan of an LED chip and cause it to dim over time.
Lifespan:
LED lights are known for having a long lifespan. But extreme heat can shorten this lifespan. If an LED light does not have enough cooling, it can easily overheat. So, this will keep it from working properly and make it last for a shorter time.
5. Common Applications of LED Lights and Heat Considerations
LED lights can be used in different settings, from lighting up your home to brightening up commercial spaces. Here are some frequent ways in which these lights are used:
Home Lighting:
You will see many homes using LED lights in lamps, ceiling fixtures, and cabinets. They are best for enclosed spaces where excessive heat could be a concern. They are okay in those areas because they don’t form that much heat.
Outdoor Lighting:
LEDs are famous for outdoor lighting, including floodlights, landscape lighting, and streetlights as well. They function properly in cooler temperatures and are very durable, so they are pretty good for outdoor use.
Commercial and Industrial Lighting:
LED lights are used for all purposes in commercial and industrial settings. You will see them in offices and even in warehouses and factories. In these spaces, heat must be managed well to make the lights work efficiently for a long time. This will also help their brightness to be consistent.
Automotive Lighting:
LEDs are mostly found in car headlights, brake lights, and interior lights. The heat formed by them should be more carefully managed in headlights. Too much heat will negatively affect its performance.
6. How to Reduce the Heat Generated by LED Lights?
LEDs give out less heat when you compare them to other sorts of lighting, but there are still a few ways in which you can eliminate the little heat that they create as well.
Choose the Right LED Bulb:
Check the wattage and brightness level when you select your LED bulb. Higher-wattage LEDs will give you more heat, so choose a bulb that fulfills your needs without being too powerful.
Maintain Proper Ventilation:
Make sure that LED lights are ventilated in a proper manner. This becomes more important for enclosed fixtures, where heat can build up and shorten their lifespan.
Use LED-Specific Dimmers:
If you are using a dimmer switch with your LED lights, it should only be made specifically for LEDs. Why, you ask? Well, traditional dimmers will make the lights overheat and will also cause flickering.
Clean Regularly:
Dust and dirt may accumulate on your LED lights if you do not take care of them. It will also reduce their ability to dissipate heat. But daily cleaning will help avoid this by keeping heat at optimum level.
Do not Overdrive:
Using an LED with more current than it’s meant to handle will make it heat up too much. So, stick to the manufacturer’s recommendations for operating current to prevent it from overheating.
![]() Strong Adsorption Capacity
Strong Adsorption Capacity
![]() Flat and Resilient Surface
Flat and Resilient Surface
![]() Easy Creative Installations
Easy Creative Installations
![]() Customizable Design Capabilities
Customizable Design Capabilities
7. Why Go for LEDSINO Products?
Selecting LEDSINO hints that you prioritize investing your money in quality and reliability. We take pleasure in delivering the best products at your doorstep. It is our job to ensure that every purchase you make meets premium standards. We have thorough quality control processes to guarantee that what you buy is the best on the market. Take pride in knowing that your purchased products are designed to function exceptionally.
Customer needs are always our priority at LEDSINO. We intend to give you a memorable experience by offering durable and long-lasting products. We are dedicated to quality, so you can rely on our products for long-lasting value and performance.
8. Our Concluding Thoughts
As we conclude this guide, we still want a definite answer to that question. Do LED lights really get that hot? Yes. But not in a way that should cause you any serious concern. We have already gone over all the important details you need to know in this article. Just remember to pick a bulb type and size that will help you be comfortable. Although LED lights do get warmer when they are on, they generally don’t get hot enough to be dangerous. With good heat management, you can make your LED lights stay bright and last for many years.
Contact
 Building D, Hongfa Science Park,
Building D, Hongfa Science Park,
2035 Songbai Road, Shiyan, Bao’an District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.