LEDs are cutting-edge tech for lighting spaces up and powering diverse electronics. LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. These semiconductors emit light when an electric current passes through them.
Over the years, LEDs have gained significant popularity due to their durability, usability, and, most importantly, their efficiency in terms of electricity conservation.
LED Evolution History
LED lighting tech is a 21st-century invention created as early as 1907 and has since developed into the LED lights we use today. LED results from phenomenal electroluminescence, which an English experimenter, Henry Joseph Round, discovered at Marconi Labs. He used a cat’s whiskey detector and a crystal silicon carbide.
Electroluminescence is an optical phenomenon in which a material emits light when an electric current is passed through it. The development of LED was not entirely a man’s invention. Instead, it was the contribution of many scientists from different areas.
Types of LED Light
LEDs have indeed revolutionized the lighting industry. This is because they are efficient and, most importantly, they provide long-lasting illumination sources. Hence, they are the ideal option for various applications, contributing to their growing popularity among people’s homes, businesses, and public spaces.
Smart LEDs
These are also known as smart light bulbs. They are the type of LEDs with wireless technology, allowing you to control them remotely. LEDs allow Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, apps, and other smart home applications to control them. They contain chips that enable them to communicate with other devices wirelessly.
Smart LEDs have several benefits, including energy savings. They consume less energy than traditional bulbs and are long-lasting. You can set them to turn on and off automatically. Lastly, smart lights or LEDs are color-changing. Users can alternate the color of light that best suits their applications.
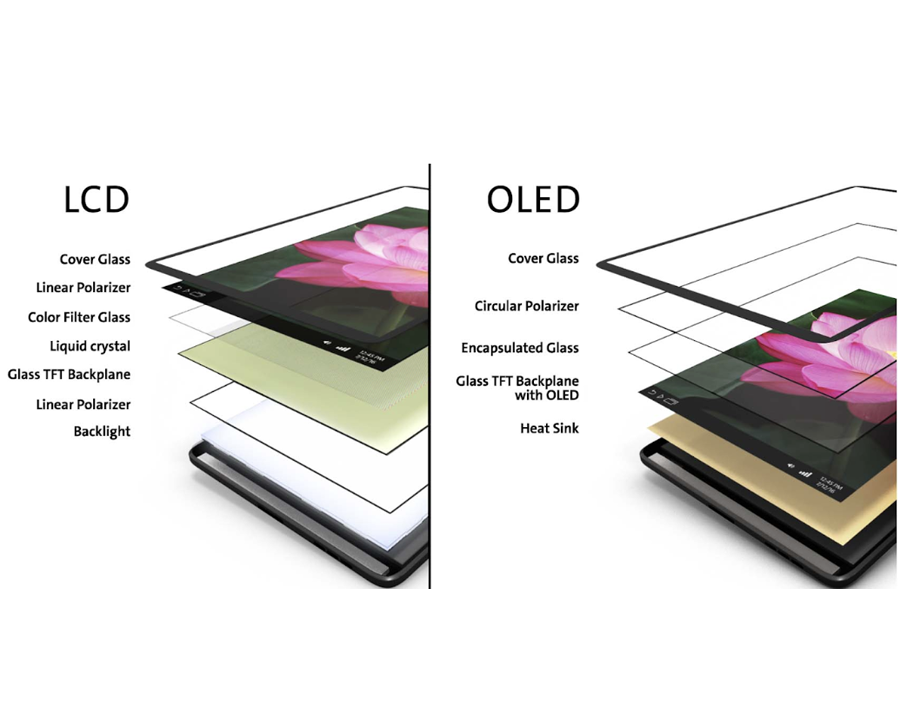
Organic LEDs
Organic LEDs, or OLEDs, illuminate when an electric current passes through a thin organic semiconductor layer. They feature carbon-based substances. OLEDs have several benefits, including the production of high-quality displays. They are also more flexible, as they can be folded, stretched, and rolled.
High-Power LEDs
These high-power light-emitting diodes can operate at currents of hundreds of mA up to more than an Amp, in contrast to other LEDs that run on tens of mA. Yet, high-power LEDs grapple with the challenge of overheating. HP-LEDs have heat sinks to facilitate heat dissipation. Failure to remove the heat leads to the device failure.
Standard LEDs
These are the most basic or most uncomplicated types of LEDs. Like all other LEDs, standard LEDs are energy efficient, compact, and have a long lifespan. They emit a single color: red, green, blue, or amber.
Standard LEDs have a voltage range of 1.7-2.0 volts for red and approximately 2.8 to up to 4.0 volts for violet. Their energy output is generally low compared to other LEDs. Standard LEDs are typical in appliances such as remote controls and displays, with simple LED needs.
Miniature LED
Miniatures light-emitting diodes are smaller than traditional LEDs. They are typically used to create displays with better contrast ratios, brightness, and energy conservation than earlier LEDs.
AC-driven LED
These are types of LEDs generated by alternating current. They can operate on AC power without a DC converter. AC-driven LEDs work so that one section emits light for every half circle, and the other is dark. Next, this action reverses in the next half cycle.
Like any LEDs, Driven LEDs are more energy efficient than traditional bulbs. Due to their energy efficiency, these types of LEDs are eco-friendly. LEDs can last up to a thousand hours, reducing the need for regular maintenance.
Strip LED
LED strips, ribbons, or tape are flexible circuit boards with SMD (Surface-Mount LEDs) and other components with adhesive backing. Traditionally, LED tapes are typical for decorative lighting, such as cove lighting, backlighting, and task lighting.
LED strip lighting emerged in the early 2000s and has increased luminous efficacy. HP SMDs have allowed them to suit applications such as fluorescent and halogen lighting fixture renewal.
How Does LED Work?
The working LED is straightforward, and the cost of production is cheap, too. That is why there was plenty of excitement when it debuted.
Simply put, an LED is a sandwich of three layers: a positive diode, a negative anode, and a transmitting material in between. When electrons flow from the anode towards the diode, some energy consumption from one medium to another. The lost energy is in the form of light and heat.
Factors that Impact LED Uses
Power Sources
The quality of the power source used can significantly impact the lifespan of the LED. Frequent power surges, voltage fluctuations, and electrical noise stress the LED constituents and eventually lead to their breaking ahead of time.
Electrical Polarity
Electrical polarity is critical in LEDs because light emission can only occur if the electrical polarity is correct. Otherwise, if the polarity is wrong, the resultant LED is reverse-biased, so minimal current flows through, and no light is produced. In addition, if the supplied voltage is high enough, incorrect polarity can cause untold damage.
Appearance
Appearance affects the use of LEDs in the sense that one considers first the color produced by the LED and then the intensity of the light produced. In contrast to traditional bulbs, LEDs emit the intended light without color filters.
People prefer excellent lighting produced in LEDs because little heat radiates in the form of IR. This, in turn, reduces the risk of damage to sensitive objects or even fabric.
Light Properties
Properties of the light emitted by LEDs, such as color, wavelength, and brightness, significantly affect their use. For example, the wavelength usually determines the color of the light produced by LEDs.
Brightness, on the other hand, is relatively directly proportional to the power within an identified range. However, high power could also lead to no light produced. Wavelength features three categories: infrared, ultraviolet, and visible. A person will consider all these light properties before choosing which LED to use.
Reliability
The reliability of an LED is critical. It affects its lifespan and how well it meets the customer’s needs. The reliability of an LED is based on the materials used to make it and the process used.
Manufacturing
As discussed, manufacturing LEDs is vital as it affects their reliability. What materials did they use to create the LED? Which process did they use? All these questions are crucial when determining the type of LED to use.
Common Applications of LED
There are several applications of LEDs, given that, over the years, LEDs have gained massive popularity. LEDs are indispensable since most of the devices we use today have LEDs. The applications include;
Indicators and signs
In indicators, LEDs provide visible lights for brakes and brake lights to be seen by other drivers. In addition to that, traffic signs above the street need to be very visible so drivers can know when to slow down or stop.
Lighting
LEDs are used in several types of lighting, including general lighting. They are bulbs that light people’s homes, businesses, and even public offices. They suit industrial, refrigerated, and outdoor lighting tasks.
Data Communication
Light can transmit data and analog signals. Because of this, LEDs are suitable for communication and signaling systems. They are also used in optic fiber cables to send data, including the cable that makes up several internet connections.
Machine Vision Systems
LEDs are typical in vision systems to provide bright light. For instance, machine vision systems such as ring lights use LED to produce a circular round light surrounding the camera lens to produce uniform illumination for a close-up image. Dome lights have LEDs to provide sufficient light for objects with high to medium reflectivity.
Biological Detection
In biological detection, UV LEDs are typical in light-induced fluorescence sensors. These sensors can identify aerosolized biological agents in as little as one minute, protecting as many people as possible.
Conclusion
LEDs are a great technology tool, not just a source of light. They have indeed changed the electronic industry, providing versatile and efficient solutions to lighting for electronic systems. Due to the various types of LEDs, engineers and designers can choose the most suitable option for their distinct applications.
Unlock Reliable LED Use with LEDSINO Now!
Do you want optimum performance and reliability in LED applications? Our guidance articles can help you make informed decisions about which light is suitable for your needs. LEDSINO is illuminating the future with strategic LED uses.
Enter the digital world with our advanced display technologies.