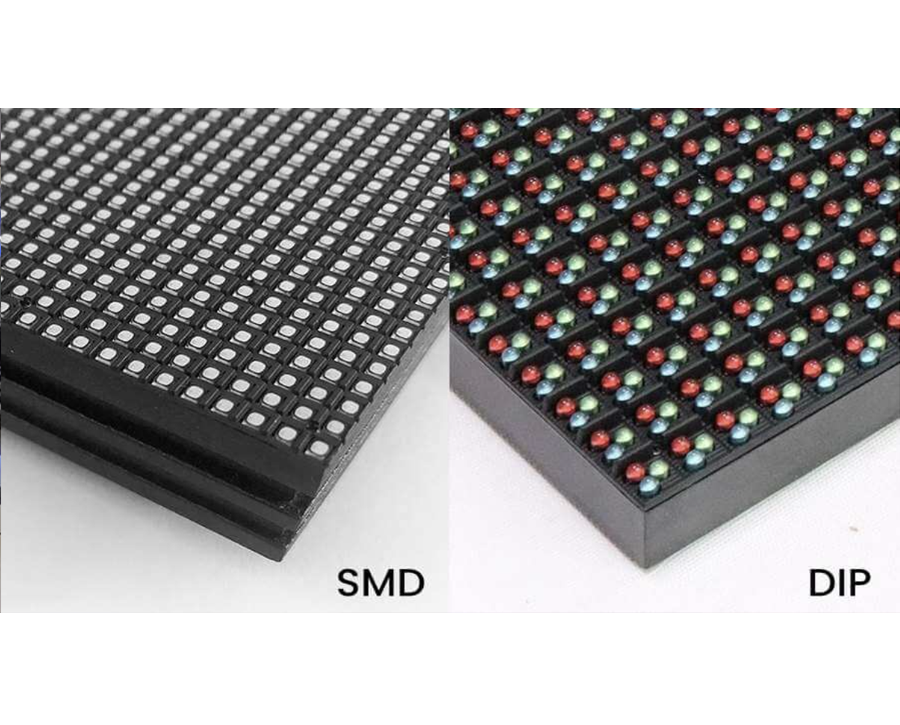
LED displays use either SMD or DIP technology which have risen to dominant positions in different applications. Despite recent display progress these two LED types continue to serve specific applications effectively. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for selecting the right solution, especially in 2025.
What Are SMD and DIP Displays?
SMD Displays
The Surface-Mounted Device technology in SMD displays combines multiple red, green, and blue diodes onto a miniature chip. A single LED chip combined with SMD technology produces many pixels in a single unit which allows screens to show sharper and more fluent images than earlier display methods.
SMD LEDs display unique pixel positioning features as these devices have predefined pixel distances. With a minimum pixel pitch of 1.5mm an SMD screen creates outstanding display quality ideal for video walls and digitally enhanced retail experiences. A p6 smd outdoor module, for instance, can provide crisp imagery for outdoor advertisements.
In corporate control rooms and broadcast studios SMD displays deliver clear colorful pictures to viewers who need to see the display from close range. SMD LEDs come in small panels and thin materials making them easy to place into minimalist design projects. This sensitive product requires managed spaces we’ll discover more about in future parts of this text.
DIP Displays
DIP led module displays use the oldest but most durable LED technology format. The pixels of these displays use separate red, green, and blue LED modules that come in epoxy containers shaped like pills. DIP LEDs show strong performance in tough and bright lighting situations because their structure fits these requirements better than SMD alternatives.
DIP technology was a successful display technology that led to major improvements but still powers critical outdoor billboard and stadium screen applications. Under strong sunlight this display produces images clearly thanks to its strong brightness output which goes beyond 10,000 nits.
Key Differences Between SMD and DIP Displays
Design and Structure
SMD and DIP Displays Have Important Design Differences
- SMD Displays: Small-scale modern displays employ RGB diodes to create a single chip which serves as light source while remaining easy to transport. Thanks to their unique design they can use tighter pixel spacing from P1.5 to P6 to provide sharp picture quality.
An SMD video wall in corporate lobbies shows detailed content through a virtually uninterrupted display because of the technology’s compact design. Because SMD LED components are tiny they need particular handling and installation methods compared to other display types.
- DIP Displays: Each separate RGB diode of DIP LEDs requires an individual protective shell resulting in a noticeably heavier construction. DIP screens handle outdoor settings perfectly because their safety-focused design rejects excessive smoothness.
DIP screens that sit next to highway billboards need to fight weather damage like dust, rain, and sunlight through many years to stay functional. These displays work better in demanding settings thanks to their bulkier form even though their size reduces their value in high-resolution close-up purposes.
Brightness and Visual Performance
Your outdoor smd led display choice relies heavily on display brightness between SMD and DIP screens. So let’s compare:
- SMD Displays: Screen technology with Surface-Mount Device design offers maximum brightness at 6,500 nits of illumination. These displays, such as a p10 smd outdoor led display options, work effectively in regular rooms at home and in shaded outdoor locations. Outdoor smd displays lose their color contrast when they face direct sun exposure.
Due to its smaller pixels an SMD screen shows better color blending at high image resolution without needing excessive brightness. An SMD video wall at a shopping mall can draw shoppers’ attention because its bright smooth imagery creates an eye-catching display.
- DIP Displays: DIP screens deliver, such as the module p5 full color outdoor display options offer superior performance in outdoor conditions thanks to their amazing brightness capacity which exceeds 10,000 nits.
Even strong daylight does not block the visibility of outdoor advertisements and stadium game scores because these screens are super bright. DIP displays shine in outdoor exposure but present visible pixelation at closer distances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMD Displays
Advantages
- High Resolution: Curved video walls using SMD LED video wall displays provide superb display accuracy and details through their small pixel pitch for retail displays broadcast studios and control room usage.
- Compact Design: Their thin and light build lets you put them anywhere while designing special video wall curves and building shapes.
- Energy Efficiency: SMD displays use less power than DIP displays mainly when used indoors.
Disadvantages
- Limited Brightness: While SMD LEDs deliver enough brightness for indoor environments they need more power to function properly in outside weather extremes.
- Vulnerability to Elements: SMD LEDs have weak resistance against environmental elements including water exposure dust and high-low temperatures which restricts their outdoor application range.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DIP Displays
Advantages
- Exceptional Brightness: DIP displays lead the outdoor sector with brightness settings higher than 10,000 nits to power billboards, stadium displays and highway signage.
- Unmatched Durability: DIP LEDs stand up to intense weather factors since they resist water exposure and block dust particles while fighting UV radiation to keep the smd digital display running reliably.
- Cost-Effective for Scale: The lower average expense of DIP displays for large outdoor displays makes these panels an accessible choice for companies that need to advertise or host events.
Disadvantages
- Bulk and Weight: Due to their larger size and heavier structure DIP LEDs prove harder to handle and set up than SMD screens.
- Lower Resolution: Large pixels in these screens reduce their resolution and make them unusable for tasks that need detailed image display.
Applications of SMD and DIP Displays
SMD Displays
The versatility of SMD displays makes them ideal for:
- Indoor Digital Signage: You will find SMD screens at their best in every type of indoor setting from shopping malls to office buildings and airport waiting areas.
- Video Walls: This technology creates perfect visuals, enabling it to serve critical roles in control room operations. SMD LED types, such as the nationstar SMD 1921, are also used for professional-grade video walls.
- Event Stages: The immersive experience created by an SMD sphere projection screen adds depth to music performances and large public events.
DIP Displays
The ruggedness and brightness of DIP displays make them a natural fit for:
- Outdoor Advertising: smd screen advertising displays from Digital Imaging Products (DIP) stand out in direct sunlight because they grab viewers’ attention wherever they are placed.
- Sports Arenas: Stadium screens display bright images thanks to DIP LEDs which operate well at long viewing distances.
- Traffic Signage: When used in outdoor settings DIP technology delivers dependable performance outdoors, such as large-scale P10 SMD LED screens for stadiums, because it stays functional throughout its lifespan.
Conclusion
Your choice between SMD and DIP displays depends entirely on your project needs. When setting up detailed picture installations inside controlled spaces at maximum resolution SMD screens prove their worth. DIP displays preserve their lead when toughness and brightness must exceed project demands in outdoor settings.
Enter the digital world with our advanced display technologies.





